Orthognathic surgery, also known as corrective jaw surgery, is a transformative procedure that aligns the jaws and teeth to improve function and facial aesthetics.
But what does this procedure entail? And who can benefit from it?
This article aims to answer these questions. It provides a comprehensive overview of orthognathic surgery, from the initial consultation to the recovery process.
We’ll discuss this surgery’s benefits for facial aesthetics and dental health and the associated risks and considerations.
Whether you’re considering orthognathic surgery, a dental professional, or simply curious, this article is for you. Let’s explore the world of orthognathic surgery together.
What is Orthognathic Surgery?
Orthognathic surgery is a type of dental surgery designed to correct issues related to jaw alignment. This procedure adjusts the jaw bones to improve overall function and appearance.
Many people suffer from jaw issues, including difficulties chewing, speaking, or breathing. Orthognathic surgery aims to resolve these functional problems.
The procedure involves repositioning the jaws. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons typically perform it, working closely with orthodontists to ensure optimal results.
A detailed assessment is required before surgery. This assessment may involve X-rays, models, and sometimes 3D imaging. It helps the surgical team create a precise surgical plan.
People who undergo orthognathic surgery often experience significant improvements. The surgery enhances chewing and speaking functions and addresses concerns related to facial aesthetics.
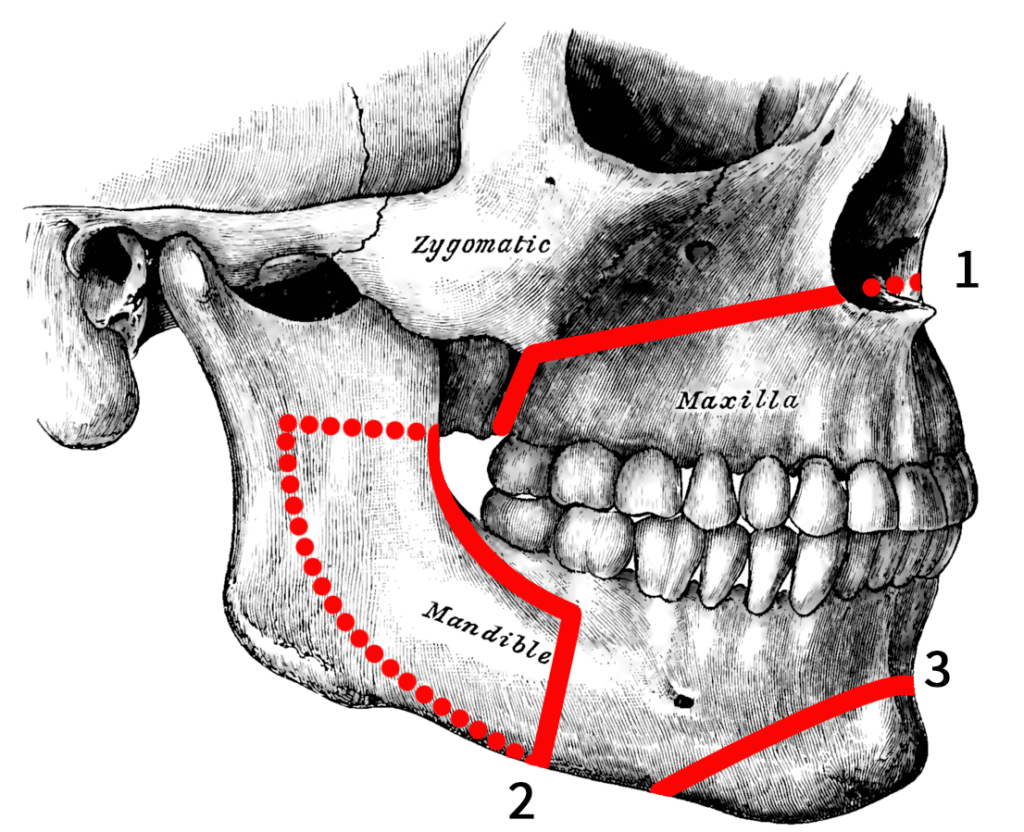
Who Needs Orthognathic Surgery?

Orthognathic surgery is often recommended for individuals with jaw misalignment. These problems can be congenital or develop due to growth abnormalities or trauma. Patients with severe overbites, underbites, or crossbites could benefit from the procedure.
People who experience difficulty chewing or swallowing might also consider this surgery. Improper jaw alignment can significantly hinder these basic functions, and corrective jaw surgery may provide a long-term solution.
Some individuals with sleep apnea may require orthognathic surgery. Misaligned jaws can obstruct the airway during sleep, and breathing issues can often be alleviated by repositioning the jaw.
Finally, those concerned with facial aesthetics might seek this surgery. The procedure improves function and enhances facial symmetry and balance. For many, the increase in confidence and quality of life is profound.
The Multidisciplinary Approach to Orthognathic Surgery
Orthognathic surgery requires collaboration among different healthcare providers. The team usually includes an oral and maxillofacial surgeon and an orthodontist, but it can sometimes include a speech therapist or a psychological counselor.
The orthodontist helps with pre-surgical and post-surgical teeth alignment. Before surgery, braces might be used to position teeth correctly. After the surgery, they ensure teeth align with the newly positioned jaws.
Surgeons rely on advanced imaging and planning tools. 3D imaging technology allows surgeons to visualize the jaw structure thoroughly, helping them devise a precise surgical plan tailored to each individual.
A psychological counselor may also be part of the team. Surgery can be emotionally challenging, so mental health support is crucial. Addressing psychological concerns better prepares patients for their surgical journey and postoperative period. This team-driven approach ensures comprehensive care for each patient’s needs.
Pre-Surgical Planning and Consultation
The first step towards orthognathic surgery is thorough pre-surgical planning. The surgeon evaluates the patient’s facial and dental structure during the initial consultation. This assessment helps determine if orthognathic surgery is appropriate.
Advanced technology plays a significant role in pre-surgical planning. Techniques like 3D imaging and computer-aided simulation are critical. These tools allow the surgical team to craft a detailed and personalized surgical plan.
Patients undergo several assessments to ensure successful surgery. These include facial measurements, dental impressions, and sometimes, X-rays. These steps provide a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s anatomy.
Key aspects discussed during the consultation include:
- Overall health assessment and medical history review
- Goals and expectations from the surgery
- Potential risks and complications
- Detailed explanation of the surgical process and recovery
This careful planning phase sets the foundation for a successful orthognathic surgery. It ensures patients are fully informed and prepared for the procedure.
Types of Orthognathic Surgeries
Orthognathic surgery encompasses several procedures, each addressing specific jaw-related issues. The choice of surgery depends on the individual’s unique needs. Surgeons tailor these procedures to improve functionality and aesthetics.
One common type is the Le Fort I osteotomy. This surgery targets the upper jaw, correcting misalignments and enhancing facial harmony. It is often used to reposition the upper jaw forward or backward.
Another prevalent procedure is bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. This surgery adjusts the lower jaw, helping correct underbites and overbites and ensuring a balanced bite.
Genioplasty is a procedure that targets the chin. It can be performed alongside other jaw surgeries, aiming to improve the overall symmetry and contour of the face.
Key types of orthognathic surgeries include:
- Le Fort I osteotomy: Repositions the upper jaw
- Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy: Adjusts the lower jaw
- Genioplasty: Alters the chin for facial balance
Understanding these different procedures highlights orthognathic surgery’s personalized approach. By using various techniques, surgeons ensure that each patient achieves their desired outcomes.
The Procedure: What to Expect During Orthognathic Surgery
Orthognathic surgery typically involves several steps performed under general anesthesia. For their comfort, patients are fully asleep during the procedure, which can last several hours, depending on the case’s complexity.
Surgeons begin by making precise incisions inside the mouth, minimizing visible scarring. They then carefully reposition the jawbones to align them appropriately.
Once the jaws are in the desired position, surgeons secure the bones. They use screws and plates to stabilize the new alignment. This ensures that the jaws remain in place as they heal.
The surgical team closely monitors the patient throughout the procedure. Advanced technology often assists in ensuring accuracy, helping to achieve optimal patient outcomes.
After the surgery, patients are transferred to recovery. Here, medical staff continue to monitor vital signs as anesthesia wears off. Patients typically stay in the hospital briefly before beginning their journey to full recovery.
Recovery and Postoperative Care
Recovering from orthognathic surgery requires patience and adherence to specific guidelines. Proper postoperative care is crucial for successful healing and overall outcomes. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions closely during this period.
Swelling and discomfort are common after surgery. These symptoms usually peak within the first few days but gradually subside. Cold compresses and prescribed medications can help manage these issues effectively.
Eating habits will temporarily change following surgery. Patients need to stick to a soft or liquid diet initially. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is vital to support healing.
Essential Postoperative Care Tips:
- Maintain oral hygiene using prescribed mouth rinses.
- Adhere to dietary restrictions as your surgeon has advised.
- Attend all follow-up appointments for monitoring and adjustments.
- Report any unusual symptoms, like persistent pain or swelling.
- Engage in recommended jaw exercises to regain mobility.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is paramount, even with dietary changes. Antibacterial mouthwashes can prevent infections. Patients must gently brush their teeth and gums as directed.
Each patient’s recovery journey varies. Consistent follow-up care with the surgical team helps ensure proper healing. Most patients return to normal activities with time and care and benefit from improved jaw function and aesthetics.
Benefits of Orthognathic Surgery for Facial Aesthetics and Dental Health
Orthognathic surgery offers significant benefits for improving facial balance and symmetry. By aligning the jaw and teeth correctly, it enhances overall facial aesthetics. This adjustment can boost a patient’s confidence and self-image.
The procedure also addresses functional issues that impact oral health. Misaligned jaws often lead to bite problems and uneven tooth wear. Orthognathic surgery resolves these by aligning the bite and reducing strain on teeth and muscles.
Breathing and speech can also improve after the surgery. Patients with jaw misalignments might experience difficulties that this surgery can rectify. By repositioning the jaw, airways and oral structures function more efficiently.
Overall, orthognathic surgery provides a comprehensive solution for aesthetic and health-related concerns. By fixing jaw problems, patients get a better bite and a nicer facial profile, significantly improving their quality of life.
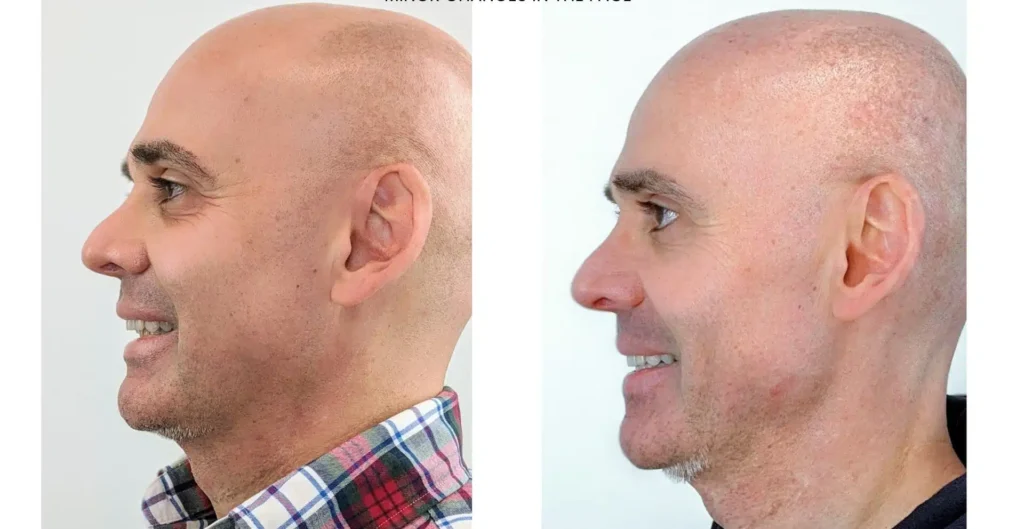
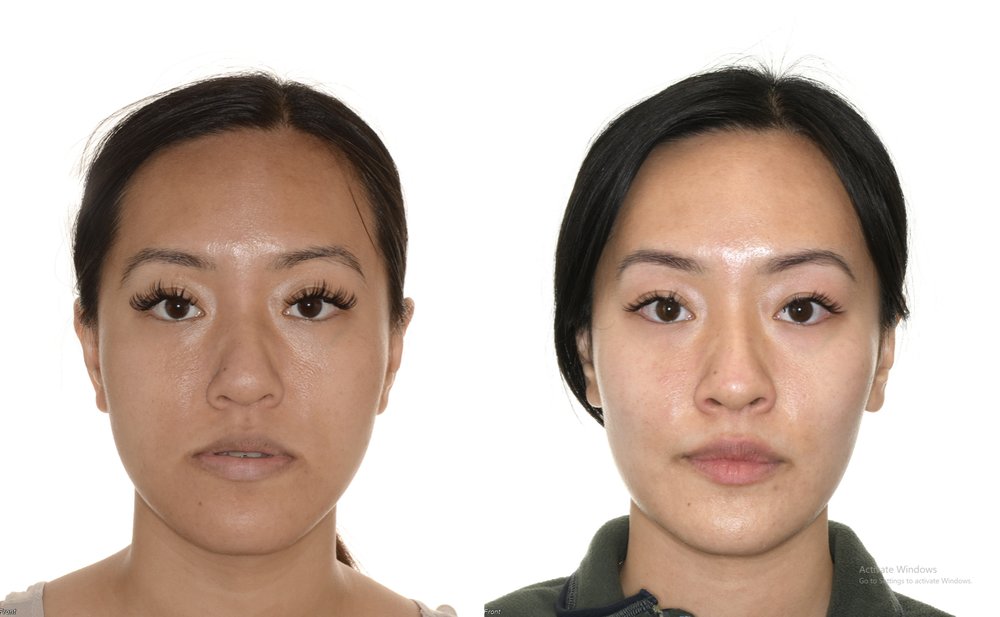
Risks and Considerations
Like any surgical procedure, orthodontic surgery carries certain risks. Potential complications include infection and nerve damage. Patients must understand these risks to make informed decisions.
There is also a chance of relapse, in which the jaw reverts to its original position. While rare, this underscores the importance of careful postoperative care. Following the surgeon’s guidelines can help minimize this risk.
Patients should thoroughly discuss all concerns with their healthcare team. Choosing a qualified and experienced surgeon significantly reduces potential risks. Understanding the procedure helps ensure a successful outcome and smooth recovery.
Patient Testimonials and Life After Surgery
Patients who undergo orthognathic surgery often share transformative experiences. Many report substantial improvements in function and aesthetics, which can lead to increased self-confidence and satisfaction.
Beyond physical changes, patients frequently notice enhanced quality of life. Easier chewing and speaking are common outcomes. This boosts overall well-being and day-to-day comfort.
Emotional impacts are also significant. Improved facial aesthetics can positively affect social interactions. Many patients express a newfound sense of happiness and confidence, which can reshape their personal and professional lives.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding orthognathic surgery and its benefits can empower individuals to make informed choices. Improving both function and aesthetics offers significant life changes.
An essential next step is consulting with a qualified surgeon. This will help you explore options tailored to your specific needs. A healthier, more balanced smile might be within reach.
To learn more about our clinic and approach to orthognathic surgery, visit our About Us page and for booking an appointment or specific details regarding our services, you can always contact us through the Contact Us page. We also invite you to explore our Reviews to hear from our satisfied patients about their transformative experiences.
